Mobile SEO: A Guide to Mobile Optimization
What is Mobile Optimization?
Updated by Chima Mmeje — November 21, 2024.
Mobile optimization is the process of ensuring that visitors who access your site from mobile devices have an experience optimized for the device.
Every year people spend more and more time on their mobile devices and tablets, but many websites still aren’t designed to account for different screen sizes and load times. With the increasing mobile usage, it is essential to ensure websites are optimized for better performance across devices. Mobile optimization takes a look at site design, site structure, SEO Best Practices for Page Speed page, and more to make sure you’re not inadvertently turning mobile visitors away.
Why is Mobile Optimization Important?
In today’s digital age, mobile optimization is no longer optional—it’s essential. With the majority of internet users accessing websites through mobile devices, businesses must ensure their digital assets are mobile-optimized. A mobile-optimized site provides a seamless user experience, which is crucial for retaining visitors and converting them into customers. By optimizing for mobile, businesses can stay competitive, improve user satisfaction, and ultimately drive revenue. Mobile optimization involves adapting websites and apps to function smoothly on various mobile devices, ensuring that users have a positive experience regardless of the device they use.
Mobile SEO Best Practices
If your site is already well-optimized for search engines, there are only a few additional things that you need to think about when optimizing for mobile devices and Google's move to mobile-first indexing.
Page speed
Because of hardware and connectivity issues, page speed is even more important for mobile users than desktop users. Beyond optimizing images, you'll want to minify code, leverage browser caching, and reduce redirects. More information on page speed can be found on our SEO Best Practices for Page Speed page.
Don't block CSS, JavaScript, or images
In the old days, some mobile devices couldn't support all of these elements, so webmasters of mobile sites blocked one or all three. But for the most part that's no longer true, and the Smartphone GoogleBot wants to be able to see and categorize the same content that users do. So don't hide it. These elements are also critical to helping Google understand if you have a responsive site or a different mobile solution.
Site design for mobile
Mobile devices are simplifying and revolutionizing the ways sites are designed, making it essential to invest in a quality mobile site. “Above the fold” no longer has meaning in a world where we scroll endlessly
Don't use Flash
The plugin may not be available on your user's phone, which means they'll miss out on all the fun. If you want to create special effects, use HTML5 instead.
Don't use pop-ups either
It can be difficult and frustrating to try and close these on a mobile device. This might lead to a high bounce rate.
Design for the fat finger
Touch screen navigation can lead to accidental clicks if your buttons are too big, too small, or in the path of a finger that's trying to get the page to scroll.
Optimize titles and meta descriptions
Remember that you're working with less screen space when a user searches using a mobile device. To show off your best work in SERPS, be as concise as possible (without sacrificing the quality of the information) when creating titles, URLs, and meta descriptions.
Use Schema markup
Because of the limited screen space, a search result with rich snippets is even more likely to stand out than on a desktop. Read more about Schema markup.
Optimize for local search
If your business has a local element, remember to optimize your mobile content for local search. This includes standardizing your name, address, and phone number and including your city and state name in your site's metadata. More information on local SEO can be found here.
Mobile site configuration
Probably the most important decision you’ll make when setting up a site is deciding whether you want to use a responsive, dynamic serving, or separate site configuration. Many small businesses are also considering mobile apps to enhance customer convenience and engagement. Each has its advantages and disadvantages. Google prefers responsive design but supports all three options as long as you have set them up properly.

Responsive web design
Responsively designed sites use CSS3 media queries to serve the same content to mobile and desktop users, using a fluid grid and a flexible design that automatically adapts to the size of a user’s screen. With the rise of mobile device usage, optimizing for mobile traffic is crucial to avoid losing potential users and to meet the expectations set by search engines that prioritize mobile-first designs.
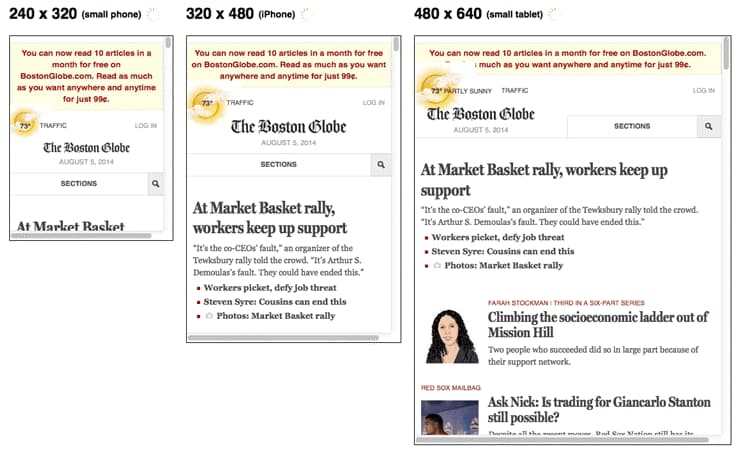
Responsive designs use media queries to target the layout based on screen width, orientation, and resolution. For example, you could use the following CSS to instruct browsers how to display content for a screen that’s 420 or fewer pixels wide:
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) are a game-changer in the realm of mobile optimization. AMP is designed to help website owners deliver fast-loading pages to mobile users, especially those with slower internet connections. By creating lightweight pages, AMP ensures that content loads quickly on mobile devices, enhancing the user experience. Implementing AMP not only improves page speed but also offers SEO benefits, as AMP pages are more likely to rank higher in search results. This can lead to reduced bounce rates and increased conversions, making AMP a valuable tool for businesses aiming to optimize their mobile presence.
Mobile-Friendly Website Features
Creating a mobile-friendly website is key to providing a smooth and enjoyable user experience. Mobile optimized sites typically feature lighter images and buttons that are appropriately sized for broader fingers, ensuring easy navigation. Text is concise and easy to read, and the conversion process involves minimal steps. Additionally, mobile sites often offer a variety of payment options, including those that don’t require entering credit card details. A simple navigation menu and the absence of intrusive popups further enhance the user experience. By incorporating these features, businesses can significantly improve user satisfaction and boost conversion rates.
Code Sample
@media screen and (max-width: 420px) { .class { [styles for this class here] }}And to link to a separate stylesheet instead, put the following HTML in between your <head> tags:
Code Sample
<link href="mobile.css" type="text/css" media="screen and (max-device-width: 480px)" rel="stylesheet"/>Responsive designs allow you to have a variety of these media queries so that users on tiny mobile screens, larger-than-average mobile screens, and even tablets can all see a site that looks designed for their devices.
Use a Google's Mobile Testing Tool to verify that your website is optimized for mobile.
Dynamic serving
If you don't have the resources for a complete site redesign or want to display different content for mobile visitors than you do for desktop ones, one solution is to use one URL to display different sets of HTML and CSS depending on what type of device your visitor is using (also called detecting user agents). This can be useful, for example, if you're a restaurant who wants a mobile visitor (who might be wandering your neighborhood) to see a sampling of reviews and a map to your location instead of your full website.
Displaying different content based on the user agent is called dynamic serving and it's done using the Vary HTTP header, which looks like this:
Vary HTTP Header
GET /page-1 HTTP/1.1Host: www.example.com(...rest of HTTP request headers...)HTTP/1.1 200 OKContent-Type: text/htmlVary: User-AgentContent-Length: 5710(... rest of HTTP response headers...)Example from the Google Developers Blog.
Simply put, this means that the content displayed will vary based on the user agent requesting the page.
Dynamic serving is not the perfect compromise that it might seem to be. For one, it relies on having an updated list of user agents, which means that every time a new mobile device comes to market that list needs to be updated. And it's not uncommon for desktops and mobile devices to be wrongly served with the HTML for the other device. Read more about common pitfalls.
Separate mobile URL
Another option is to create a second, parallel site for mobile users. This allows you to create completely custom content for mobile visitors. To avoid URL confusion, most parallel mobile sites use an "m" subdomain.
Parallel mobile sites can be as imperfect as dynamic serving sites at sending visitors to the right version, so be sure to make it easy for visitors who end up in the wrong place to click over to their preferred experience.
You'll also want to make sure that your site redirects are all in place and as lean as possible to decrease page speed. And to avoid duplicate content issues, you'll need to set up rel="canonical".
How to Optimize Your Website for Mobile Devices
Optimizing a website for mobile devices involves several crucial steps. First and foremost, businesses should implement responsive web design, which allows the site to adapt to different screen sizes and devices seamlessly. Next, using a behavior analytics tool can help identify friction points and areas for improvement. Building mobile-friendly website features, such as lighter images and appropriately sized buttons, is also essential. Additionally, creating Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) can enhance page speed and reduce bounce rates. By following these steps, businesses can ensure their website is optimized for mobile devices, providing a superior user experience.
Test Your Site Using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Tool
Testing your website’s mobile-friendliness is a critical step in the optimization process. Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool is an excellent resource for determining whether your site meets Google’s standards for mobile pages. The tool provides insights into how mobile-friendly your site is and offers recommendations for improvement. By regularly testing your site, you can ensure it delivers a smooth and efficient user experience for mobile users, which can positively impact your search engine rankings and overall online performance.
Keep Learning
- The SEO's Guide to Building a Great Mobile Site: Kristina Kledzik lays out why you need a mobile solution now and offers insight into what options work best for different types of sites.
- The Definitive Guide to Google's New Mobile SEO Rules: Peter McLachlan outlines what Google is looking for in a mobile-optimized site.
- Mobile Emulator: This tool lets you see what your site looks like on a wide variety of mobile devices.
- Responsive Web Design Testing Tool: See what your responsive site looks like on a variety of standard screen sizes.
- Screaming Frog: Check your redirects by analyzing your site with this tool.
- Building Smartphone-Optimized Websites: Official advice from Google on how to get your mobile site in order.
Put your skills to work
Download MozBar
The MozBar SEO toolbar shows you relevant metrics right in your browser, as you surf the web.